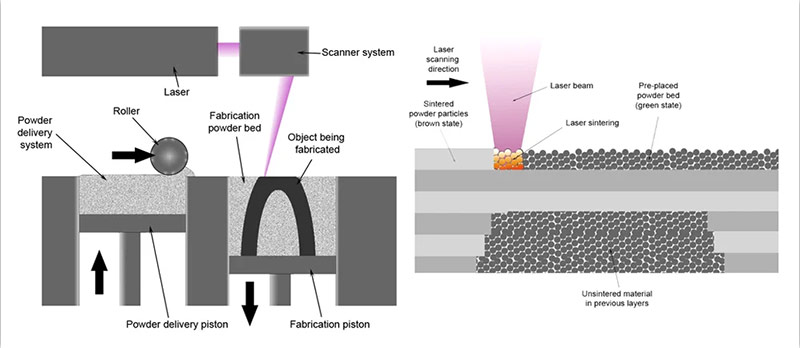
Materials
Industries
Providing a wide range of applications and solutions for various industries.
Industries
Automotive
Automotive grade certified precision parts.
Industrial machinery
Multiple material choices make industrial parts more competitive.
Medical and Dental
Medical grade certified precision parts.
Aerospace & Aviation
Precision manufacturing boosts aerospace development.
Consumer electronics
First choice for new product launches.
Robotics
Accelerate the development of the future robotics industry.
3D Printing Industries
3D Printing for Automotive
Transform processes and enable customized and innovative automotive parts.
3D Printing for Medical and Dental
Personalized healthcare solutions and
specific treatments.
3D Printing for Cultural Creativity
Promote the innovation and development of
cultural and creative industries
3D Printing for Industrial
Driving progress and innovation in
manufacturing